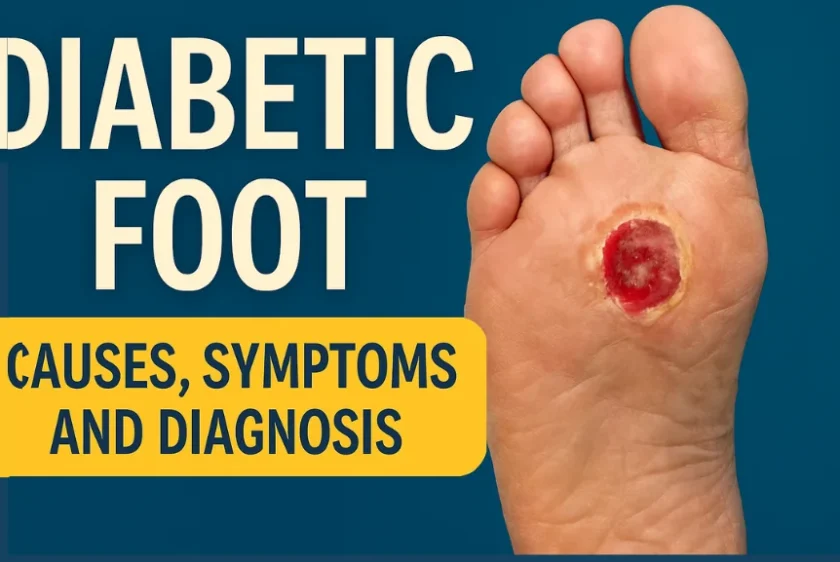
What is a Diabetic Foot?
A Diabetic Foot refers to foot complications caused by high blood sugar levels that damage nerves and blood vessels. This can lead to infections, ulcers, slow healing, and severe diabetic foot pain.
Quick Summary
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition | Diabetic Foot |
| Common Symptoms | Pain, numbness, swelling, slow-healing wounds |
| Main Causes | Neuropathy, poor circulation, infections |
| Diagnostic Tests | Sensory test, ABI, Doppler, X-ray |
| Risk Level | High for uncontrolled diabetes |
| Related Keywords | Diabetic Foot Pain, Diabetic Foot Care, Diabetic Foot Treatment |
Causes of Diabetic Foot
Understanding what triggers diabetic foot problems helps in early prevention.
1. Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
High blood sugar damages nerves, leading to:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Burning sensation
- Loss of protective feeling
2. Poor Blood Circulation
Reduced blood flow delays healing, increasing infection risk.
3. Foot Ulcers
Minor injuries can become deep wounds if untreated.
4. Infections
Weak immunity makes infections spread quickly.
5. Dry & Cracked Skin
Dryness causes cracks that allow bacteria to enter.
6. Improper Footwear
Tight shoes cause pressure points, increasing diabetic foot pain and ulcers.
Symptoms of Diabetic Foot
| Symptom | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Numbness | Due to nerve damage |
| Tingling or burning | Sign of neuropathy |
| Diabetic Foot Pain | Sharp, constant, or shooting pain |
| Dry/Cracked skin | Skin loses moisture |
| Color changes | Redness, dark patches, or bluish tone |
| Swelling | Sign of infection or circulation issue |
| Slow healing | Poor blood flow delays recovery |
| Black skin patches | Sign of dead tissue – emergency |
Diagnosis of Diabetic Foot
Doctors perform various evaluations to diagnose diabetic foot conditions.
1. Physical Examination
- Foot shape
- Skin condition
- Nail health
- Presence of ulcers
2. Sensory Testing
Tools like monofilament assess nerve function.
3. Circulation Tests
- ABI (Ankle-Brachial Index)
- Doppler Ultrasound
These check blood flow and detect blockages.
4. Lab Tests
- Blood sugar levels
- Wound culture (if needed)
5. Imaging
- X-ray for bone infection
- MRI for deep tissue evaluation
Causes vs Symptoms vs Diagnosis
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Causes | Neuropathy, poor circulation, infections |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, color changes, ulcers |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, ABI, Doppler, X-ray |
Risk Factors for Diabetic Foot
These factors increase the chances of developing diabetic foot:
- Long-term diabetes
- Uncontrolled blood sugar
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Overweight
- Poor footwear
- Lack of diabetic foot care
Essential Diabetic Foot Care Tips
Even though your title does not require treatment, including Diabetic Foot Care improves ranking for your provided keyword.
Daily Foot Care Checklist
| Activity | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Foot Inspection | Check for cuts, redness, cracks daily |
| Cleaning | Wash gently and dry completely |
| Moisturizing | Apply lotion (avoid between toes) |
| Footwear | Use soft, wide, comfortable shoes |
| Toenails | Trim straight to avoid ingrown nails |
| Avoid Walking Barefoot | Prevents injuries |
| Sugar Control | Keeps circulation and nerves healthy |
Diagnosis Tests
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Monofilament Test | Checks nerve sensation |
| ABI | Measures blood circulation |
| Doppler Ultrasound | Detects blood flow issues |
| Wound Culture | Checks infection type |
| X-Ray | Detects bone infection (Osteomyelitis) |
| MRI | Assesses deep tissue damage |
When to See a Doctor?
Seek immediate help if you notice:
- Persistent diabetic foot pain
- A wound that does not heal in 7–10 days
- Blackened skin
- Swelling or pus
- Fever or spreading redness
These may indicate a serious infection requiring urgent diabetic foot treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the first sign of a diabetic foot?
Numbness, tingling, or a slow-healing wound.
2. Does diabetic foot always cause pain?
Not always. Due to nerve damage, some patients feel no diabetic foot pain.
3. How is a diabetic foot diagnosed?
Through physical exam, sensory tests, ABI, Doppler, and imaging.
4. Can diabetic foot be prevented?
Yes. Proper diabetic foot care reduces risks significantly.
5. What is the best treatment for diabetic foot?
Early cleaning, wound dressing, antibiotics, nerve pain control, and circulation improvement. In severe cases, surgery may be needed.